Written by Dennis Sven Mittmann
Table of Contents:
1. Screenshots
2. Installing on Windows Pc
3. Installing on Linux
4. System Requirements
5. Game features
6. Reviews
This guide describes how to use Steam Proton to play and run Windows games on your Linux computer. Some games may not work or may break because Steam Proton is still at a very early stage.
1. Activating Steam Proton for Linux:
Proton is integrated into the Steam Client with "Steam Play." To activate proton, go into your steam client and click on Steam in the upper right corner. Then click on settings to open a new window. From here, click on the Steam Play button at the bottom of the panel. Click "Enable Steam Play for Supported Titles."
Alternatively: Go to Steam > Settings > Steam Play and turn on the "Enable Steam Play for Supported Titles" option.
Valve has tested and fixed some Steam titles and you will now be able to play most of them. However, if you want to go further and play titles that even Valve hasn't tested, toggle the "Enable Steam Play for all titles" option.
2. Choose a version
You should use the Steam Proton version recommended by Steam: 3.7-8. This is the most stable version of Steam Proton at the moment.
3. Restart your Steam
After you have successfully activated Steam Proton, click "OK" and Steam will ask you to restart it for the changes to take effect. Restart it. Your computer will now play all of steam's whitelisted games seamlessly.
4. Launch Stardew Valley on Linux:
Before you can use Steam Proton, you must first download the Stardew Valley Windows game from Steam. When you download Stardew Valley for the first time, you will notice that the download size is slightly larger than the size of the game.
This happens because Steam will download your chosen Steam Proton version with this game as well. After the download is complete, simply click the "Play" button.
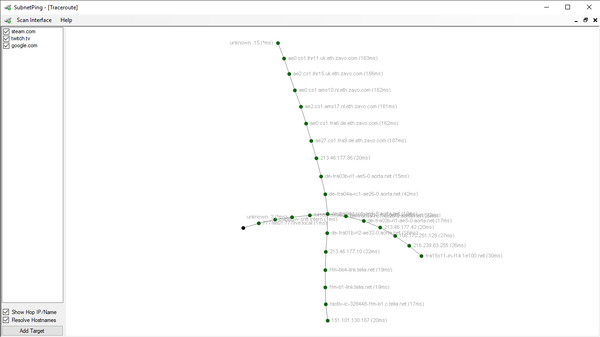
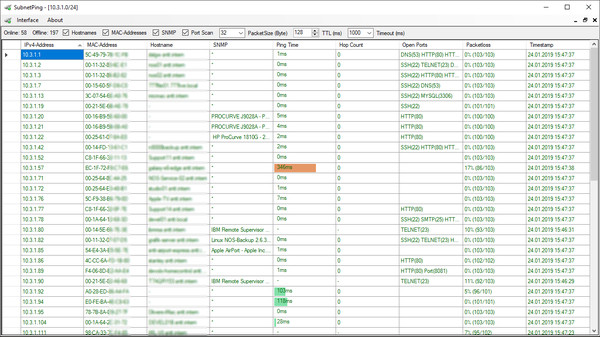
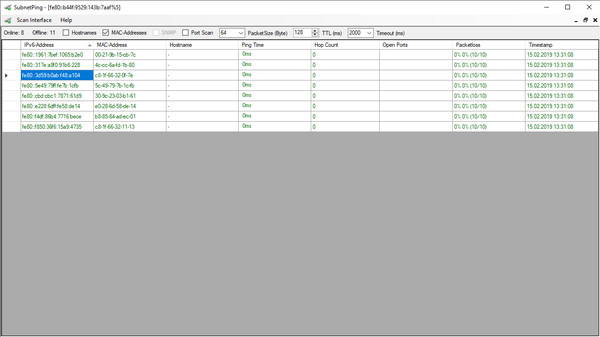
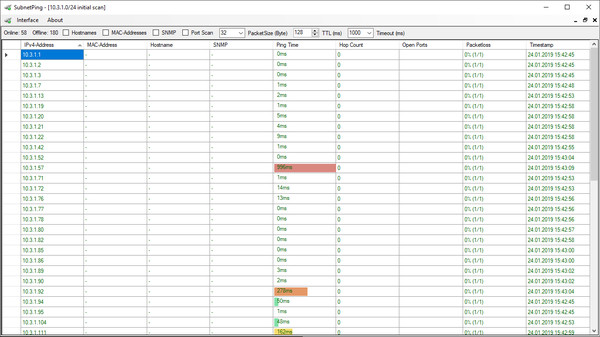
SubnetPing is a handy tool to get information about used IP-addresses in an IPv4 network.
SubnetPing is a small but useful tool to determine information about used IPv4-addresses in an IPv4 network.